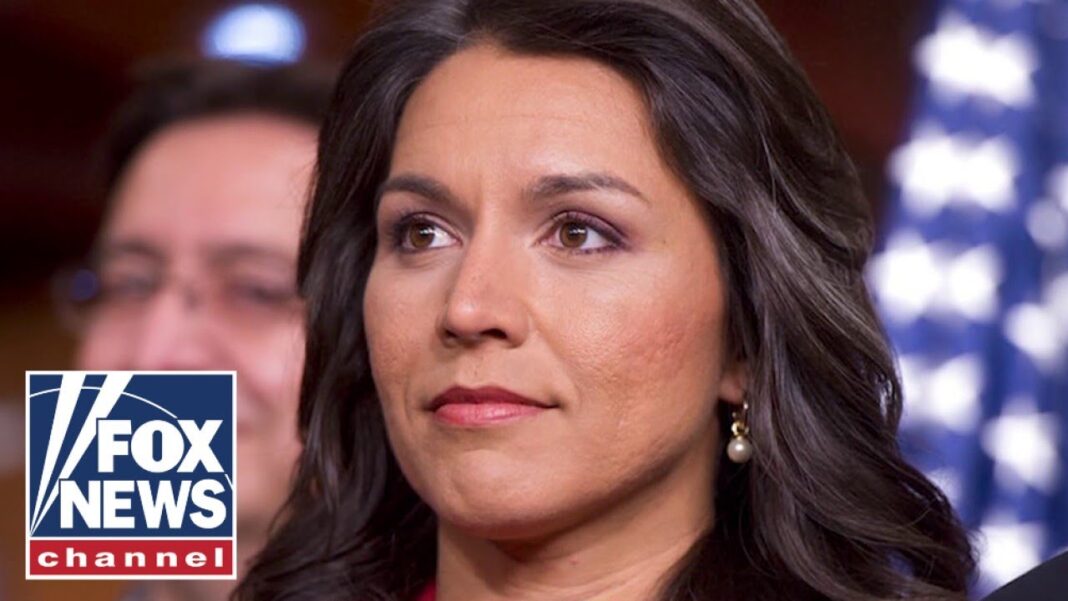
The final vote to confirm Tulsi Gabbard to the position of director of national intelligence will likely take place Feb. 11 or Feb. 12.
The Senate voted on Feb. 10 to invoke cloture on the nomination of Tulsi Gabbard to the position of director of national intelligence, bringing the former congresswoman one step closer to confirmation.
The 52–46 vote means senators have 30 hours to debate the nomination before taking a final vote on Gabbard’s confirmation.
Senate Democrats are unlikely to yield their debate time in an effort to slow down the confirmation process of President Donald Trump’s political appointees, which means the final vote will likely come either late on Feb. 11 or early on Feb. 12.
Gabbard’s nomination to lead the nation’s intelligence community was highly scrutinized during the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence’s initial public hearing on the matter on Jan. 30.
Lawmakers from both sides of the aisle expressed skepticism about Gabbard’s fitness for the role, given her previous support for intelligence leaker Edward Snowden and her previous opposition to a law that allows the federal government to indirectly collect intelligence on U.S. citizens without a warrant.
Gabbard ultimately prevailed in the committee’s initial round of voting, securing a party-line vote of 9–8 after convincing Sens. Susan Collins (R-Maine) and Todd Young (R-Ind.) to give their endorsement.
Gabbard assured the committee that she would not pardon Snowden unless directed to do so by the president. She acknowledged that the former National Security Agency intelligence contractor broke the law, but she refused to describe him as a “traitor.”
She said she supported Snowden’s efforts in exposing previously unknown programs through which the government solicited the assistance of tech companies to spy on U.S. citizens.
Likewise, Gabbard said she had reconsidered her position on FISA 702, a controversial law that allows U.S. intelligence agencies to indirectly collect the sensitive private information of U.S. citizens during surveillance of foreign targets.