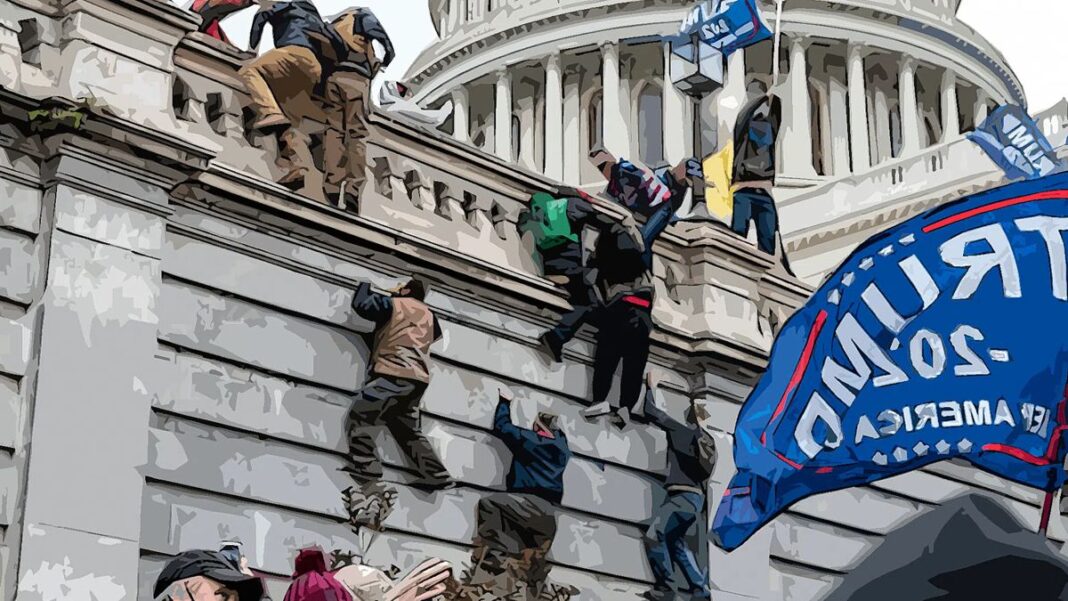
A year after the attack on the Capitol, data scientists say artificial intelligence can help forecast insurrection — with some big concerns
For many Americans who witnessed the attack on the Capitol last Jan. 6, the idea of mobs of people storming a bedrock of democracy was unthinkable.
For the data scientists who watched it unfold, the reaction was a little different: We’ve been thinking about this for a long time.
The sentiment comes from a small group working in a cutting-edge field known as unrest prediction. The group takes a promising if fraught approach that applies the complex methods of machine-learning to the mysterious roots of political violence. Centered since its inception a number of years ago on the developing world, its systems since last Jan. 6 are slowly being retooled with a new goal: predicting the next Jan. 6.
“We now have the data — and opportunity — to pursue a very different path than we did before,” said Clayton Besaw, who helps run CoupCast, a machine-learning-driven program based at the University of Central Floridathat predicts the likelihood of coups and electoral violence for dozens of countries each month.
The efforts have acquired new urgency with the recent sounding of alarms in the United States. Last month, three retired generals warned in a Washington Post op-ed that they saw conditions becoming increasingly susceptible to a military coup after the 2024 election. Former president Jimmy Carter, writing in the New York Times, sees a country that “now teeters on the brink of a widening abyss.” Experts have worried about various forms of subversion and violence.
Election misinformation soared to 10,000 posts per day in Facebook groups before Jan. 6
The provocative idea behind unrest prediction is that by designing an AI model that can quantify variables — a country’s democratic history, democratic “backsliding,” economic swings, “social-trust” levels, transportation disruptions, weather volatility and others — the art of predicting political violence can be more scientific than ever.
Some ask whether any model can really process the myriad and often local factors that play into unrest. To advocates, however, the science is sufficiently strong and the data robust enough to etch a meaningful picture. In their conception, the next Jan. 6 won’t come seemingly out of nowhere as it did last winter; the models will give off warnings about the body politic as chest pains do for actual bodies.
“Another analogy that works for me is the weather,” said Philip Schrodt, considered one of the fathers of unrest-prediction, also known as conflict-prediction. A longtime Pennsylvania State University political scienceprofessor, Schrodt now works as a high-level consultant, including for U.S. intelligence agencies, using AI to predict violence. “People will see threats like we see the fronts of a storm — not as publicly, maybe, but with a lot of the same results. There’s a lot of utility for this here at home.”
CoupCast is a prime example. The United States was always included in its model as a kind of afterthought, ranked on the very low end of the spectrum for both coups and election violence. But with new data from Jan. 6, researchers reprogrammed the model to take into account factors it had traditionally underplayed, like the role of a leader encouraging a mob, while reducing traditionally important factors like long-term democratic history.
Its risk assessment of electoral violence in the United States has gone up as a result. And although data scientists say America’s vulnerability still trails, say, a fragile democracy like Ukraine or a backsliding one like Turkey, it’s not nearly as low as it once was.
“It’s pretty clear from the model we’re heading into a period where we’re more at risk for sustained political violence — the building blocks are there,” Besaw said. CoupCast was run by a Colorado-based nonprofit called One Earth Future for five years beginning in 2016 before being turned over to UCF.
Another group, the nonprofit Armed Conflict Location & Event Data Project, or ACLED, also monitors and predicts crises around the world, employing a mixed-method approach that relies on both machine-learning and software-equipped humans.
“There has been this sort of American exceptionalism among the people doing prediction that we don’t need to pay attention to this, and I think that needs to change,” said Roudabeh Kishi, the group’s director of research and innovation. ACLED couldn’t even get funding for U.S.-based predictions until 2020, when it began processing data in time for the presidential election. In October 2020, it predicted an elevated risk for an attack on a federal building.
Meanwhile, PeaceTech Lab, a D.C.-based nonprofit focused on using technology in resolving conflict, will in 2022 relaunch Ground Truth, an initiative that uses AI to predict violence associated with elections and other democratic events. It had focused overseas but now will increase efforts domestically.
“For the 2024 election God knows we absolutely need to be doing this,” said Sheldon Himelfarb, chief executive of PeaceTech. “You can draw a line between data and violence in elections.”The science has grown exponentially. Past models used simpler constructs and were regarded as weak. Newer ones use such algorithmic tools as gradient boosting, which fold in weaker models but in a weighted way that makes them more useful. They also run neural networks that study decades of coups and clashes all over the world, refining risk factors as they go.
“There are so many interacting variables,” said Jonathan Powell, an assistant professor at UCF who works on CoupCast. “A machine can analyze thousands of data points and do it in a local context the way a human researcher can’t.”
Many of the models, for instance, find income inequality not to be correlated highly with insurrection; drastic changes in the economy or climate are more predictive.